Detailed Exploration of Causes of Cracked Cylinder Heads and Preventive Measures
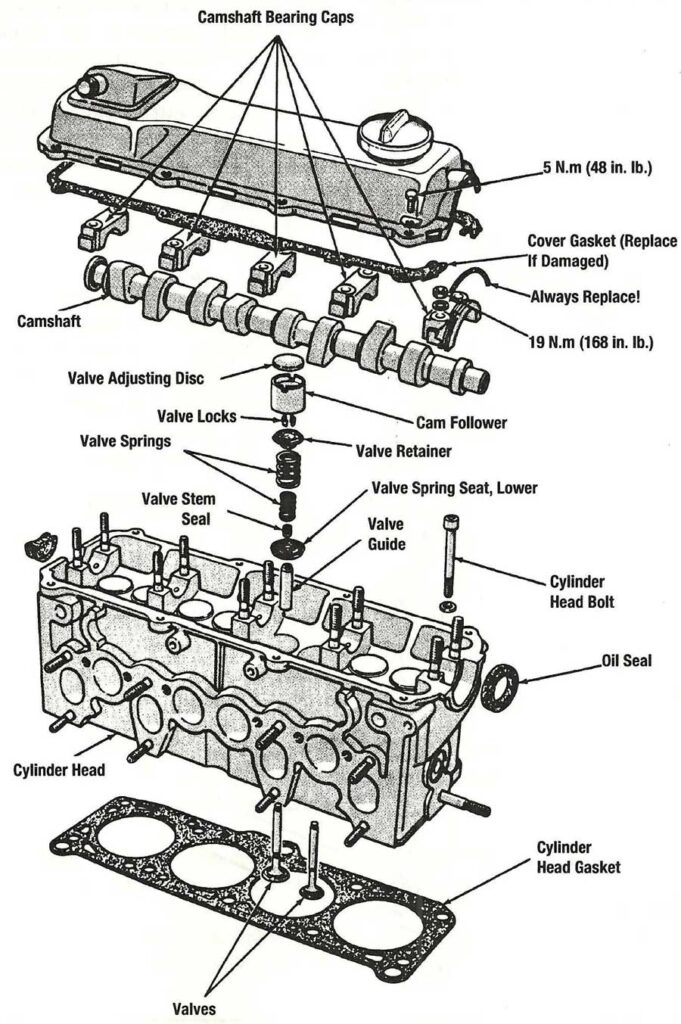
The cylinder head is a critical component in diesel engines, playing a pivotal role in managing combustion and sealing the combustion chamber.
However, encountering a cracked cylinder head can lead to severe consequences such as coolant loss, compression issues, and significant repair costs.
In this comprehensive discussion, we delve into the primary causes of cracked cylinder heads and effective preventive strategies to maintain engine reliability and longevity.
Causes of Cracked Cylinder Heads
1. Extreme Temperature and Pressure
Cracks in cylinder heads often stem from the relentless combination of high temperatures and pressures within the combustion chamber.
The material of the cylinder head, under prolonged exposure to these conditions, gradually weakens and forms cracks.
This compromises the structural integrity and performance of the engine over time.
2. Impact on Valves
Aside from causing cracks in the cylinder head, extreme operating conditions also adversely affect valves. Valves can stretch, break, or suffer from chordal fractures due to the intense thermal and mechanical stress.
These conditions lead to reduced clearance between valves and rocker arms, accelerating wear and potentially compromising engine efficiency and performance.
3. Underlying Issues
Cracks in cylinder heads are rarely isolated incidents caused solely by material defects.
Often, underlying engine issues such as blown head gaskets or problems with liner protrusion contribute significantly.
Addressing these foundational problems promptly is crucial to preventing the occurrence of cylinder head cracks and ensuring prolonged engine health.
4. Engine Deletions
While illegal and not endorsed, engine modifications or deletions aimed at enhancing performance can inadvertently increase the likelihood of cylinder head cracks.
Modifications like adjusting horsepower calibrations can disrupt engine timing and lead to elevated cylinder pressures.
This heightened stress on the cylinder head can eventually manifest as cracks, underscoring the importance of adhering to legal guidelines and maintaining the integrity of engine components.
Prevention of Cylinder Head Cracks
1. Reducing Cylinder Pressure and Temperature
Here’s how various strategies can be applied:
Optimizing Combustion Parameters:
Adjusting fuel injection timing and air-fuel ratios can optimize combustion efficiency.
This not only improves engine performance but also reduces the peak temperatures reached during combustion, thereby lowering thermal stress on the cylinder head.
-Utilizing modern engine management systems that monitor and adjust these parameters in real-time can further enhance efficiency and reduce wear on engine components.
Proper Cooling System Maintenance:
– Ensuring the cooling system is well-maintained is critical. This includes regular inspection and cleaning of radiators, ensuring coolant levels are adequate, and replacing coolant at recommended intervals.
– Efficient cooling prevents overheating of the cylinder head and other engine components, which is essential for preventing cracks caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
High-Quality Coolant Usage:
– Regular coolant analysis and monitoring of corrosion inhibitors can prevent coolant degradation, which can otherwise lead to overheating and potential damage to engine components.
In the context of excavators and tractors, where engines are subjected to heavy workloads and adverse environmental conditions, implementing these measures is not only preventive but also cost-effective.
By reducing cylinder pressure and managing temperature effectively, operators can minimize the risk of cylinder head cracks and ensure prolonged engine durability.
This proactive approach not only enhances equipment reliability but also reduces downtime and maintenance costs associated with premature engine failures.
Proper Engine Calibrations
When modifying engine performance, it is essential to ensure that adjustments are harmonious and do not compromise the structural integrity of the cylinder head.
Properly calibrated engines experience reduced stress levels and operate more efficiently, reducing the risk of cracks and other mechanical failures.
Addressing Other Contributing Factors
In the context of excavators and tractors, cylinder head cracks seldom stem solely from material defects.
Often, underlying engine issues such as blown head gaskets or problems with piston ring protrusion contribute significantly.
Promptly addressing these foundational problems is crucial to prevent cylinder head cracks and ensure prolonged engine health.
Excavators and tractors operate under high loads and in harsh environments, increasing the risk of component wear and damage.
Issues like blown head gaskets or piston ring protrusion can create uneven pressure and thermal stress on the cylinder head, exacerbating the formation of cracks.
Once cracks occur, they negatively impact machine performance and efficiency, potentially leading to more severe mechanical failures.
Therefore, maintaining and regularly inspecting excavator and tractor engines are critical tasks to ensure reliability and durability.
Timely detection and resolution of underlying issues such as blown head gaskets significantly reduce the likelihood of cylinder head cracks, extending engine lifespan and performance.
In summary, engine maintenance for excavators and tractors is not merely about repairs but also an investment in mechanical health and long-term performance.
Professional maintenance practices mitigate failure risks, ensuring equipment operates efficiently and reliably under varying work conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding the root causes of cracked cylinder heads and implementing proactive measures are essential for maintaining diesel engine performance and longevity.
By addressing underlying issues, adhering to proper maintenance protocols, and adopting optimal driving habits, engine owners can effectively reduce the risk of cylinder head cracks.
This comprehensive approach not only enhances engine reliability but also minimizes the likelihood of costly repairs and downtime. Ensuring the integrity of the cylinder head is integral to sustaining the overall health and efficiency of diesel engines in various operational environments.
