For individuals learning to operate an excavator, a comprehensive understanding of its various components is essential for success on any project
While the specifics may vary across different models, the fundamental elements remain consistent, whether operating a mini or a skid steer excavator.

When delving into the intricate anatomy of an excavator, one can categorize its parts into three primary sections: the undercarriage, cab, and arm/boom. Let’s delve into a detailed exploration of the components of an excavator and their respective functions.
The Cab: Operative Center of the Excavator
The excavator’s cab stands as the central control area of the machine, providing the operator with a comfortable and functional workspace. It shelters the control console, seating, and often important operational features such as air conditioning and heating systems
This integral section also affords 360-degree visibility, equipped with glass windows and sometimes additional safety features. The cab serves as the operational nerve center, ensuring the operator’s ability to manage and maneuver the excavator effectively.

The Function and Importance of the Track Frame
Excavators, renowned for their versatility and power, exhibit a complex design that encompasses various critical components. One such crucial element is the track frame,
an integral part of the undercarriage, playing a pivotal role in ensuring the excavator’s stability and maneuverability.
Importance of the Track Frame
The track frame is of paramount importance due to its significant impact on the excavator’s functionality. By distributing the machine’s weight evenly, the track frame minimizes the risk of tipping or getting stuck,
thereby enhancing the excavator’s performance and safety. Moreover, the stability and traction provided by the track frame are critical when operating in demanding conditions such as construction sites, mining areas, and various terrains where traditional wheeled vehicles may struggle to maintain traction and stability.
In essence, the proper functioning of the track frame is indispensable for the overall efficacy and safety of the excavator, making it a fundamental component essential for the successful completion of diverse engineering tasks.
In conclusion, the track frame stands as a fundamental element within the excavator’s undercarriage, essential for maintaining stability, distributing weight, and ensuring smooth operations in challenging environments.
Its significance cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the excavator’s overall performance, making it a vital cog in the machinery’s wheel of functionality.
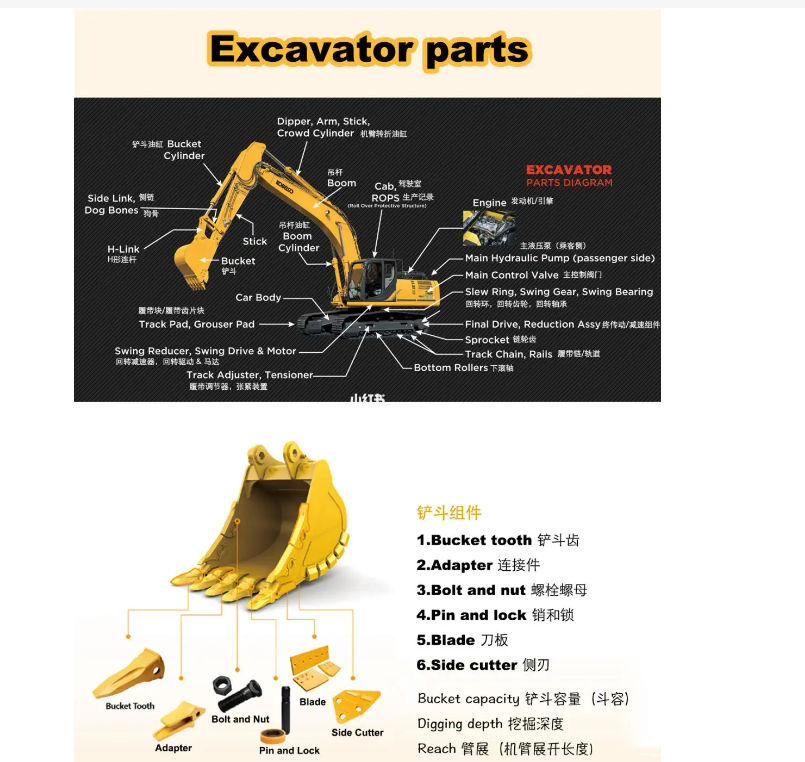
Track Components: Pads, Chains, Shoes, Bolts
The track assembly of heavy machinery such as excavators and bulldozers is a complex system comprising several crucial components, each playing a vital role in ensuring the machine’s stability, traction, and overall functionality. Among these essential track components are pads, chains, shoes, and bolts, which together form the backbone of the track system.
1.Pads
Pads are the parts of the track that come into direct contact with the ground. They are designed to endure substantial wear and tear while providing traction and support.
These pads are crucial in ensuring that the machinery maintains grip and stability on various surfaces, including loose soil, gravel, and uneven terrain.
Moreover, the design and material composition of the pads significantly impact the machine’s ability to exert force without sinking and to navigate challenging landscapes effectively.
2.Chains
The chains are the continuous loop of links connecting the drive sprocket and the idler wheel, propelling the machinery forward or backward. These links are meticulously engineered to withstand heavy loads,
continuous stress, and abrasion. The durability and flexibility of the chains directly influence the machine’s capacity to navigate rugged terrains, pull heavy loads, and maintain consistent speed and direction, making them a critical component of the track system.
3.Shoes
Shoes act as the track’s support structure, providing a stable base for the entire track assembly. These components are designed to distribute the machine’s weight evenly and endure significant pressure during operation.
Properly designed and maintained shoes are crucial for ensuring the track’s integrity and preventing premature wear and damage to other components, ultimately enhancing the machinery’s overall stability and longevity.
4.Bolts
Bolts are responsible for securing the various components of the track system, including pads, chains, and shoes, ensuring that they remain firmly attached during operation.
The strength and integrity of these bolts are essential in maintaining the cohesion of the track system, preventing dislodgment and minimizing the risk of potential hazards or disruptions during heavy-duty tasks.
The Importance of the Cabin as the Operational Center
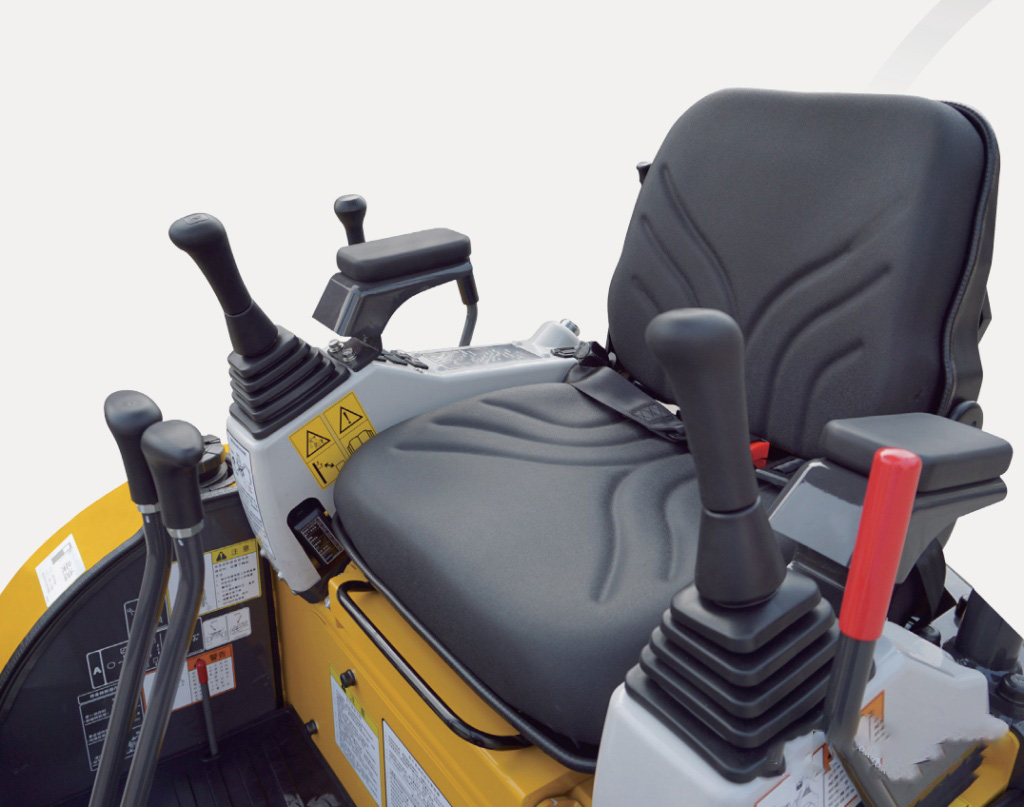

Within heavy machinery such as excavators, cranes, and bulldozers, the cabin serves as the nerve center, housing the operator and a host of controls, interfaces, and systems crucial for efficient and safe operation.
The significance of the cabin as the operational center cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the productivity, safety, and comfort of the equipment operator.
Control Hub and Interface
The cabin functions as a centralized control hub, housing an array of levers, joysticks, pedals, and touchscreens, allowing the operator to manipulate the machine’s various functions with precision and ease.
These controls enable the operator to maneuver the equipment, operate attachments, manage hydraulic systems, and carry out intricate tasks with accuracy.
Additionally, the cabin often integrates advanced technologies such as GPS, telematics, and monitoring systems, providing the operator with real-time data and insights for improved decision-making.
Operator Comfort and Safety
The design and layout of the cabin are meticulously crafted to prioritize the comfort and safety of the equipment operator. Ergonomic seating,
climate control, noise insulation, and visibility enhancements are incorporated to mitigate operator fatigue, reduce distraction, and ensure clear lines of sight, thereby promoting a safe and secure operational environment.
Furthermore, modern cabins are equipped with safety features such as rollover protection structures (ROPS) and falling object protection structures (FOPS) to shield the operator from potential hazards, reinforcing the cabin’s role as a sanctuary for the equipment operator.
Environmental Adaptability
The cabin provides a controlled environment, shielding the operator from external elements such as extreme temperatures, dust, and noise pollution.
This controlled environment not only enhances operator comfort but also allows for sustained productivity, especially in adverse weather conditions or challenging work environments.
The ability to maintain a consistent and comfortable working environment within the cabin is essential for sustaining operator efficiency and attentiveness during extended operational periods.
In essence, the cabin stands as the operational nucleus of heavy machinery, offering a secure and supportive environment for the equipment operator to effectively and safely manage the equipment and its diverse functionalities.
The integration of advanced technologies further elevates the role of the cabin, transforming it into an intelligent command center that facilitates precise and informed decision-making.
In conclusion, the cabin’s significance as the operational center is undeniable, as it directly influences the productivity, safety, and well-being of the equipment operator.
As technological advancements continue to enhance cabin design and functionality, its role as the epicenter of heavy machinery operation becomes increasingly pivotal, underscoring its indispensable importance within the realm of heavy equipment.
The Core Function, Role, and Importance of Excavator Boom

In the realm of heavy machinery, the excavator boom stands out as a pivotal component, instrumental in the machine’s overall functionality and effectiveness. Its core functionality, diverse capabilities, and overall importance underline its indispensable role within the realm of excavation and construction equipment.
Core Functionality
The excavator boom, as the elongated arm extending from the machine, serves as the primary manipulator for excavation and material handling.
It provides the necessary reach, depth, and precision for digging, lifting, and placing materials, making it an essential component for a wide range of construction and earthmoving tasks.
The ability to articulate, extend, and pivot the boom greatly enhances the machine’s operational versatility, allowing it to access hard-to-reach areas and carry out tasks with efficiency and accuracy.
Versatility and Capabilities
The boom’s adaptability enables it to accommodate various attachments such as buckets, rippers, grapples, and hydraulic breakers, expanding its capabilities beyond excavation to include tasks such as demolition, material handling, and site preparation.
This versatility underscores the boom’s role as a multifunctional tool, amplifying the machine’s utility and making it an indispensable asset across diverse construction and earthmoving projects.
Safety and Efficiency
The boom’s design and engineering prioritize operator safety and equipment efficiency. Built-in safety features and structural integrity ensure the stability and reliability of the boom, mitigating risks associated with heavy loads and dynamic operational conditions.
Additionally, the boom’s control mechanisms and hydraulic systems are designed for precise and responsive operation, facilitating the achievement of rapid, accurate, and safe excavation and material handling activities.
In summary, the excavator boom stands as the quintessential instrument for excavation and material handling within the domain of heavy machinery.
Its core functionality, adaptability, and critical role in enhancing operational efficacy and safety position it as a cornerstone component of modern construction and earthmoving equipment.
In conclusion, the boom’s significance in driving operational efficiency, project performance, and operator safety highlights its indispensable importance within the realm of heavy machinery, reaffirming its status as an essential and irreplaceable asset in the field of construction and excavation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Below are some of the most common questions regarding the components of an excavator.
How many parts does an excavator have?
The number of parts in an excavator varies depending on the specific model. While the exact count can differ, the majority of excavators typically consist of 22 fundamental components, as mentioned earlier.
What is the end of an excavator called?
The end section of an excavator is known as the bucket. This essential attachment is primarily utilized for excavating, digging into the earth, and lifting materials.
What is the arm of an excavator called?
The arm of an excavator is referred to by several names, including the arm, dipper, or stick. This critical part of the excavator is responsible for reaching out and is instrumental in manipulating attachments for digging and lifting operations.
